1. Make a list of all programming languages and Web development tools used by you in prior experiences. Describe what you know about Web application frameworks before we begin.
Lists:
a.) Develop Php by using Dreamweaver MX, CSS Validator, HTML Validator andLink Checker
b.) Develop Servlet by using java studio creator and UML.
Ruby on Rails is an MVC style framework which enables rapid development of web applications using the Ruby language. The code itself is often described as 'short and elegant, yet powerful' and the concepts and features within Ruby on Rails take this elegance to a new level for web development.
2. Ruby is “an interpreted scripting language” for quick and easy object-oriented programming”. Find out about the Ruby language and discover what this means.
Find info from http://www.gsp.com/cgi-bin/man.cgi?section=1&topic=ruby
GSP.COM states that Ruby's features are as follows:
- Interpretive (Ruby is an interpreted scripting language)
Ruby is an interpreted language, so you don't have to recompile programs written in Ruby to execute them. - Variables have no type (dynamic typing) ( quick and easy object-oriented programming)
Variables in Ruby can contain data of any type. You don’t have to worry about variable typing. Consequently, it has a weaker compile time check. - No declaration needed (quick and easy object-oriented programming)
You can use variables in your Ruby programs without any declarations. Variable names denote their scope, local, global, instance, etc. - Simple syntax ( quick and easy object-oriented programming)
Ruby has a simple syntax influenced slightly from Eiffel. - No user-level memory management (quick object-oriented programming)
Ruby has automatic memory management. Objects no longer referenced from anywhere are automatically collected by the garbage collector built into the interpreter. - Everything is an object (object-oriented programming)
Ruby is the purely object-oriented language, and was so since its creation. Even such basic data as integers are seen as objects. - Class, inheritance, and methods (object-oriented programming)
Of course, as an object-oriented language, Ruby has such basic features like classes, inheritance, and methods. - Singleton methods (quick and easy object-oriented programming)
Ruby has the ability to define methods for certain objects. For example, you can define a press-button action for certain widget by defining a singleton method for the button. Or, you can make up your own prototype based object system using singleton methods, if you want to. - Mix-in by modules (quick and easy object-oriented programming)
Ruby intentionally does not have the multiple inheritance as it is a source of confusion. Instead, Ruby has the ability to share implementations across the inheritance tree. This is often called 'Mix-in'. - Iterators ( quick and easy object-oriented programming)
Ruby has iterators for loop abstraction. - Closures (quick and easy object-oriented programming)
In Ruby, you can objectify the procedure. - Text processing and regular expression
Ruby has a bunch of text processing features like in Perl. - Bignums
With built-in bignums, you can for example calculate factorial(400). - Exception handling
As in Java(tm). - Direct access to the OS
Ruby can use most Unix system calls, often used in system programming. - Dynamic loading (Ruby is an interpreted scripting language)
On most Unix systems, you can load object files into the Ruby interpreter on-the-fly.
Therefore, Ruby is “an interpreted scripting language” for quick and easy object-oriented programming”.
3. What is Rails and how does it work with Ruby?
Ruby is an object-oriented scripting language which combines features of Perl and Smalltalk. The Rails framework provides a number of conventions that reduce complexity and the possibility of errors in the construction of basic client-server web applications. It uses standard libraries for client-side UI features and also for standard database structure.
4. What is meant by “convention over configuration” in regards to the use of Rails in Web application development?
Eweek.com (http://www.eweek.com/c/a/Application-Development/Ruby-on-Rails-Making-Programmers-Happy/) tells me that "Convention over configuration.,Instead of telling various parts of the technology stack five, six, seven times that you have a products table thats the data source of your product object, weve institutionalized that convention in a generalized notion: Classes are singular, tables are plural. This may sound like a trivial notion, but it has a radical impact on the amount of work that the programmer needs to do in his daily work. Were basically taking the whole world of pain that is known as configuration and making it optional. As long as you do what most people want to do most of the time, you get a free ride. No configuration necessary. So get the 80 percent by convention, tailor the last 20 percent by hand. "
5. When did Model-View-Controller begin and where is it used?
Wiki (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model-View-Controller ) tells me that MVC was first described in 1979[1] by Trygve Reenskaug, then working on Smalltalk at Xerox PARC. Model–view–controller (MVC) is an architectural pattern used in software engineering. Successful use of the pattern isolates business logic from user interface considerations, resulting in an application where it is easier to modify either the visual appearance of the application or the underlying business rules without affecting the other.
6. Describe the steps involved with the MVC design approach.
Wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model-View-Controller) tells me that
MVC encompasses more of the architecture of an application than is typical for a design pattern.When considered as a design pattern, MVC is fundamentally the same as the Observer pattern. There are three step for MVC desigen.
The first step - Define Model
Is the domain-specific representation of the information on which the application operates. Domain logic adds meaning to raw data (for example, calculating whether today is the user's birthday, or the totals, taxes, and shipping charges for shopping cart items).
Many applications use a persistent storage mechanism (such as a database) to store data. MVC does not specifically mention the data access layer because it is understood to be underneath or encapsulated by the model.
The second step - Define View
Renders the model into a form suitable for interaction, typically a user interface element. Multiple views can exist for a single model for different purposes.
The third step - Define Controller
Processes and responds to events (typically user actions) and may indirectly invoke changes on the model.


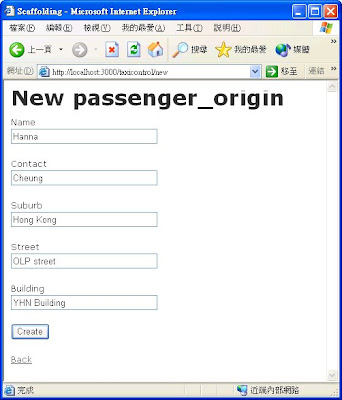
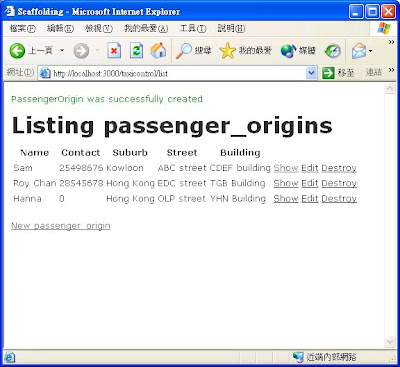 Figure 3.
Figure 3.
